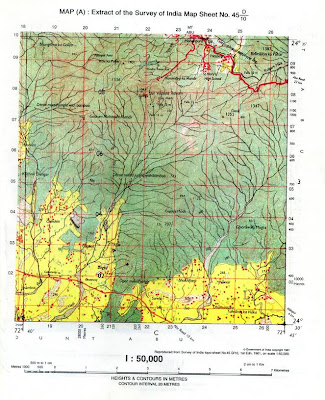
Hello,
See the features of this toposheet. Divide the toposheet into 4 quarters. Study the each quarter. For example North west corner (A), North East Corner (B), South West Corner(c) and South East Corner (D). For example what features do you see in the A Corner???First of all, you see river Sipu, a few nucleated settlements, yellow wash, open scrub, little bit of green forest on top of A corner, we can see some spot heights too. Can you see a cart track (red line)? We can also see perennial wells (blue). Did you spot stony waste (8596)? In the same way, go through the B corner and C corner and D corner. Make a mental picture of the toposheet with prominent symbols. After having a quick glance of thetoposheet, read the questions that are asked. You have 15 minutes to read the question paper. First read the other questions and then come to the toposheet which requires more time to read. Keep a pencil ready to mark few features.For the bigger view of the toposheet, click on top of the picture.
- Can you see R.F.? You can see at the bottom right. R.F. is 1:50,000. I have already explained to you how to write R.F. in the earlier lesson.
- can you see the scale? You can see almost near the R.F. The scale is 2cm to 1 km. It means 2cm on the map is equal to the 1km on the ground. Good, i suppose u understood.
- What's the contour interval of the toposheet? Check the contour interval near the scale. Contour interval of this toposheet is 20 metres.(usually it is 20 metres)
- What else can you see? Ok, let's do the direction which i have explained to you earlier. Find out what is the directionof Rajkot lie from Gangudra? First of all, Rajkot is in grid square 8995 and gangudra is in grid square 8793. Imagine you are in Gangudra and you want to go to Rajkot from Gangudra? First of all, you hv to go up which is north and then you have to turn right, which is east direction.Therefore the comapass direction is north-east from Gangudra. Do you follow?
- Where do you find the lowest part in the toposheet? The south west corner is the lowest part in the map. because two rivers flow towards south west whichis an indication of the slope. check the spot heights in the map. they are decreasing towards south west. Identify some spotheights in the map.
- See the settlements on the map: What type of settlement do you find? Ofcourse, nuclear/compact/clustered. If you didnt understand, read the text book on settlements and come back to the blog.
- What kind of rainfal this area gets? check the rivers-we can see broad sandy bed exposed, a thin water channel, (in blue) several cart tracks, and a pack track. This shows that the area gets seasonal rainfall.
- Now let us see the occupation. Study the toposheet closely. I had told you about the occupations. Go through it again. Let us study the occupation of Bhadli (Jhat) - grid square 8596. What do you notice there? click the toposheet and check. its is A CORNER. There is a river, perennial wells (Blue dots), yellow patch(which means agriculture) and stony waste. Can you see them? From this we know that the occupation of the people of that area is cultivation and stone cutting or extraction of limestone. This is indicated by the presence of agricultural land ( in yellow colour), perennial wells and the presence of lime kilns.
- It is a clustered settlement too.
- Can you see the irrigation facilities or source of water? We can see the river which has narrow blue line which means it is perennial even though the river is seasonal. Then we also can see the perennial wells. So two perennial source of water is the River waters and well irrigation.
- Let's study man made features - we can see few temples in the toposheets and permanent huts. I couldn't see any post office. As I have told you, my eyes are not very sharp. In the exam, they will ask one or two man-made features. So the man-made features are temples and permanent huts.
- Now let's study the natural features - We can see rivers, trees, islands in the middle of the river, jungles, mines, pack tracks, cart tracks, lined wells, etc. You can see all these in this map. So, you select any two. The natural feature is river and forest. Sometime they will give a grid square and ask to you to mention one man-made feature and one natural feature. Go and locate that grid square and follow the points that I have told you.
- Let us see the drainage pattern on the map. See the area around the town Gangudra.(Grid square 8793) See the drainage pattern around the area-dont see only in the grid square 8793. Go beyond that. The river or drainage pattern is Rectangular or Trellised. Can you see the shape of the river? Thin lines that join the main river. Read the text book regarding the drainage pattern (if you have not understood) There are three drainage patterns - Dendritic(Tree like or veins of a leaf) Trellis/Rectangle and Radial.
- Let us study the river bed of Sipu- In what two ways does the river bed of Sipu convey that it flows through a region of seasonal rainfall? We did go through that earlier. Study the river. It has a broad sandy riverbed which is exposed. If you dont understand the sandy river bed, go to the text book and looks for the symbos of sandy bed. You will see it in my blog too. It also has a thin water channel in the middle of the river. We also see many cart and pack tracks passing the river. Therefore, the river doesn't have much water in the summer season and so the river dries up. Do you follow me? Since the river is dry, you see the sandy beds and cart and pack tracks passing the river. So the people can cross the river during summer. Therefore it is a seasonal river.(it means the river gets water only in the rainy season).
- What are the conventional sighs near north east part of the toposheet near open mixed jungle? - check corner B - We find broken ground there. So what is broken land? Broken land gives rise to Bad land topography. These are generally found along the banks of a river. Broken ground is caused due to erosion during rain when the river is in flood. It usually heappens in the area where there is no vegetation/plants.
- Some time a question comes on the comparision of two settlements. Now let us study the village Jigol (grid square 8590) and other villages. Jigol is better off than other settlements. It has good transport system in comparision with other villages. We can see many cart tracks leading into the village. Plus it has many lined wells for irrigation purposes.
- In which quarter of the map extract do you find the lowest area to be? Divide the whole toposheet into 4 corners. We have done that in the beginning. Look for the spot heights in the toposheet. if you study the heights, you will find south west qurater of the map are decreasing towards the south west. See also the river flowing. They flow towards the south west. So the south-west corner of the map exatract is the lowest region.
- Hope you know how to find grid squares - 4 figure or 6 figure/digit grid reference. Find four digit grid square is easy but the problem begins when you have to find 6-digit grid reference. When you are asked to locate the 6-digit reference, rememeber these points. First find the square. Ok, let us locate a place using 6-figure grid reference of a temple in the north east of Odhava. Ok, let us see the 4-figure grid reference. It is in the grid square 8992. This is four figure grid reference. now we need 6-figure grid reference. After locating 4-figure grid reference, divide that square into 4 equal parts. First take a ruler and place it on the horizontal line of that grid square(. get the mid point. Then place the ruler on the vertical line and find the mid point and join these mid points. then u get the mid point of easting and northings. then u locate the spot in the grid square and if the spot is beoynd the mid point, then it wil be above 5. You can find the exact 6 figure grid reference by dividing grid squares into 10 blocks. Hold the scale vertical and horizontal on that grid square and join them. Now u get 10 X 10 equal squares. NOw you see where is the spot and give the grid reference.894925